STCW
STCW Explained
The Standards of Training, Certification & Watchkeeping Convention (STCW) sets the requirements that all seafarers need to achieve certification.
The STCW Convention
STCW was first implemented in 1978. Following some important amendments over the years, notably in 1995, it came into full effect in 2002. In June 2010, at the Diplomatic Conference in Manila, Philippines, the latest revision of the STCW will be debated and formalised into adocument that will set the international standards for seafaring best practice now and in the future.
STCW certification was created to promote safety of life and property at sea and to protect the marine environment. It establishes internationally accepted standards of training and certification of seafarers, ensuring that crew are qualified and fit for duties at sea.
STCW Basic Safety certificates are a requirement for virtually all professional seafarers.
The level of certification and training you are required to have is based on the capacity in which you serve and the type of vessel you work on.
Three levels of responsibility
Management
Masters, Chief Mates, Chief Engineers and Second Engineer Officers.
Operational
- Serving as an officer in charge of a navigational or engineering watch or as designated duty engineer for periodically unmanned machinery spaces or as radio operator on board a seagoing ship, and
- Maintaining direct control over the performance of all functions within the designated area of responsibility in accordance with proper procedures and under the direction of an individual serving in the management level for that area of responsibility.
Support
Ratings.
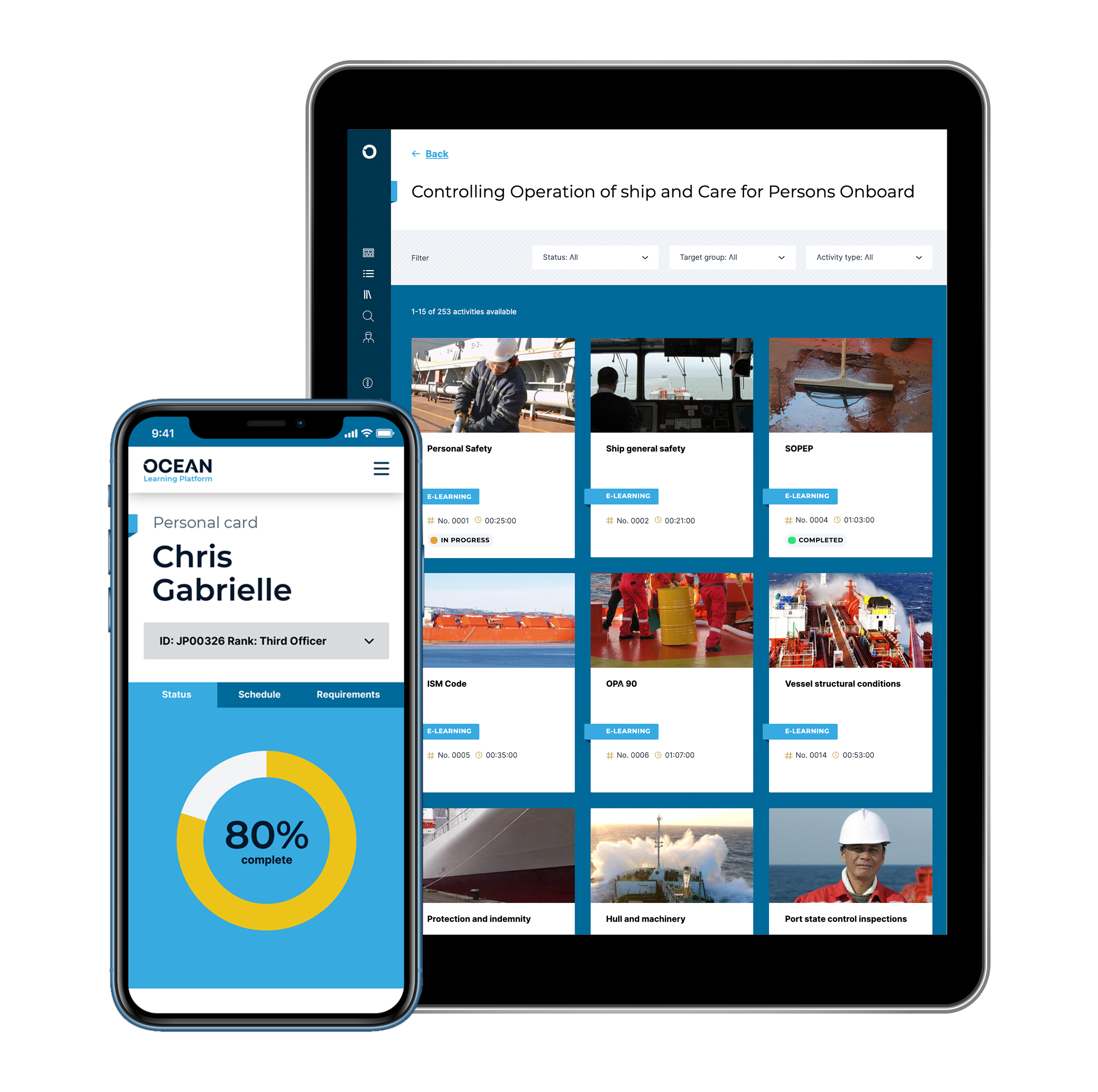
The codes for STCW compliant licences or certificates are divided by sections, departments and levels. We made our Ocean Learning Library with the STCW structure in mind.
Discover an unparalleled breadth and quality of content
Over 800 blended learning titles